Last updated on July 17th, 2023 at 01:11 pm
In the fascinating world of language, numerous diverse languages exist with unique structures, vocabulary, and grammar. However, linguists have identified commonalities that transcend individual languages amidst this rich tapestry of linguistic diversity.
These common features, known as linguistic universals, provide valuable insights into the nature of human communication and the underlying principles that govern language acquisition and use.
In this article, we will explore some of these linguistic universals, shedding light on the shared traits that make all languages fundamentally interconnected.
What is Linguistic Universal?
Quick Navigation
A linguistic universal refers to a common feature or characteristic that can be observed across different languages. These universals provide insights into the underlying principles and structures that exist in human languages, transcending the specific details of individual languages.
They represent fundamental traits shared among all languages, highlighting humans’ innate language acquisition ability and the common patterns found in phonology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics.
Linguistic universals serve as a foundation for understanding the nature of human communication and the interconnectedness of languages, fostering cross-cultural understanding and appreciation for linguistic diversity.
Most Common Linguistic Universals
Let’s walk you through some of the most common linguistic universals across different languages.
1. The Innate Language Acquisition Ability
One of the most remarkable linguistic universals is the inherent human capacity for language acquisition. From birth, infants possess an innate ability to acquire language, regardless of the specific language they are exposed to.
This universal characteristic suggests that humans are biologically predisposed to acquire language, supporting the notion that language is an integral part of human nature.
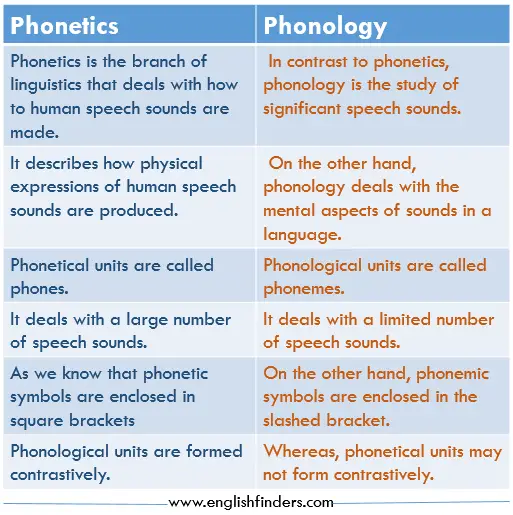
2. Phonological Patterns and Sound Systems
Another linguistic universal lie in the organization of sounds within languages. Although individual languages have unique phonetic inventories, underlying patterns and constraints govern the formation and organization of sounds.
For example, all languages have a limited set of phonemes, which are the distinct sounds that differentiate words. Furthermore, phonological patterns such as consonant-vowel structures and syllable structures are found across various languages.
3. Syntactic Structures and Grammar
The structure of sentences and the rules governing word order and sentence formation represent another set of linguistic universals. While languages may differ in their specific word orders and grammatical rules, they all share a basic underlying structure.
For instance, nearly all languages employ subject-verb-object (SVO) or subject-object-verb (SOV) word orders to convey meaning. This universal pattern indicates that certain sentence structures are more natural and intuitive for human communication.
4. Semantic Concepts and Word Meaning
Linguistic universals also extend to the realm of meaning and word semantics. Although languages may possess different vocabularies, they often share common concepts that can be expressed through similar words or lexical categories.
For instance, the existence of color terms across various languages suggests a universal human perception of colors. Similarly, categorizing objects and actions into nouns and verbs is prevalent in almost all languages.
5. Pragmatic Principles and Communicative Intentions
The way in which language is used for communication also exhibits universal characteristics. Pragmatic principles, such as the cooperative principle and the maxims of conversation, guide effective communication across cultures and languages.
These principles emphasize clarity, relevance, and efficiency in conveying intended meanings, facilitating successful interaction among individuals.
6. Cultural Influences on Language
While linguistic universals highlight the commonalities among languages, it is important to acknowledge the influence of culture on language variation. Cultural factors shape language through vocabulary choices, idiomatic expressions, and social norms that affect communication styles.
Therefore, while languages may share fundamental features, they also exhibit unique cultural nuances and expressions that reflect the diversity and richness of human societies.
Final Thoughts
Linguistic universals provide valuable insights into the shared features that underlie human languages. The innate language acquisition ability, phonological patterns, syntactic structures, semantic concepts, pragmatic principles, and the interplay between language and culture all contribute to the tapestry of linguistic diversity.
By understanding these commonalities, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of languages and the human capacity for communication. Language is a remarkable reflection of our shared human experience, transcending borders and fostering understanding across cultures.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are linguistic universals present in all languages?
Yes, linguistic universals are common features that can be observed across different languages. While languages may have unique characteristics, underlying principles and structures are shared among all languages.
How do linguistic universals relate to language acquisition?
Linguistic universals highlight the innate language acquisition ability of humans. Individuals possess a natural predisposition to acquire language regardless of the specific language. These universals shed light on the fundamental mechanisms involved in language learning and use.
Do linguistic universals apply to spoken and written languages alike?
Yes, linguistic universals apply to both spoken and written languages. The shared features encompass various aspects of language, including phonological patterns, syntactic structures, semantic concepts, and pragmatic principles. These features are present in both oral and written forms of communication.
How do cultural influences impact linguistic universals?
Cultural influences play a significant role in language variation and expression. While linguistic universals highlight commonalities, languages also reflect specific communities’ unique cultural nuances and social norms. Cultural factors shape vocabulary choices, idiomatic expressions, and communication styles within a given language.
What insights can linguistic universals provide us about human communication?
Linguistic universals provide valuable insights into the nature of human communication. By studying these common features, we gain a deeper understanding of the shared traits that make all languages interconnected. It helps us recognize language’s fundamental principles, fostering better cross-cultural understanding and effective communication.

Azizul Hakim is the founder & CEO of englishfinders.com. He is a passionate writer, English instructor, and content creator. He has completed his graduation and post-graduation in English language and literature.