Last updated on June 20th, 2025 at 10:04 am
Sentences are the fundamental parts of English grammar. It’s difficult to understand English grammar without learning the basics of different types of sentences and how they are formed. In this lesson, we’ll analyze simple, complex, and compound sentences to help you understand them better. Let’s start with the definition of a sentence.
What is a Sentence?
Quick Navigation

In simple words, we can say that a sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought or idea. It typically consists of a subject and a predicate, the subject refers to the person or thing performing the action while the predicate refers to what the subject is doing.
Types of Sentences
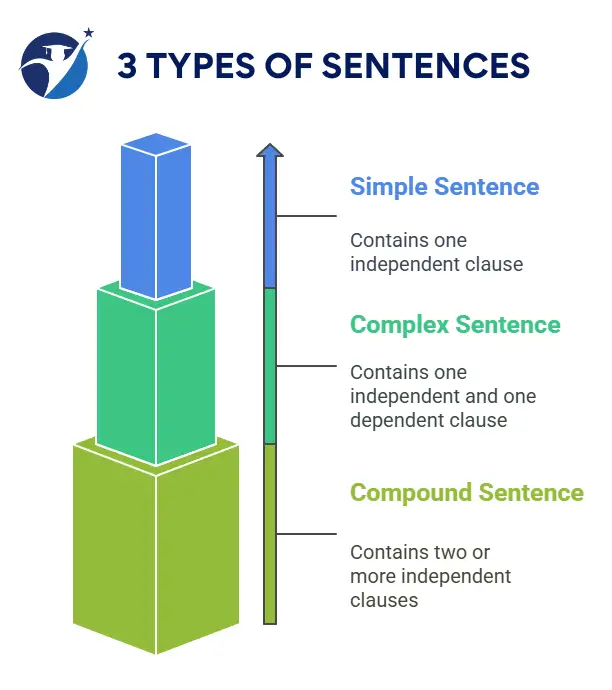
We already know that sentences are divided into many categories or types, and we can divide sentences into three types according to their structure: simple, complex, and compound.
Before knowing the definitions of all these sentences, we need to learn more about clauses and phrases. Let us see the definitions and examples of clauses and phrases in English grammar.
Clauses
A clause consists of a group of words that contains a subject and a finite verb. To get a clear conception of clauses, let us see some examples:
- I obey my responsibility.
- My parents love me so much.
- I have a daughter.
- He is my favorite friend.
- Austen cooks delicious food.
Note: All the sentences contain a subject and a finite verb.
Types of Clauses
Clauses are of three types. They are:
- Principal clause
- Subordinate clause
- Co-ordinate clause
1. Principal Clause
A clause that has independent meaning and can be used independently is called a principal clause. For example:
- I know the boy very well.
- He sees a bird.
- She goes to the market.
- Reema felt sick.
- I love fast food.
2. Subordinate Clause
A subordinate clause is a clause with no independent meaning and cannot be used independently. A subordinate clause depends on other clauses to complete its purpose. For example:
- Though he is poor, he is honest.
- I know a boy who is a brilliant student.
- I had a pen which I had lost.
- He reads a book, though he doesn’t understand the meaning.
- I love my mother, who loves me too.
All the underlined clauses are subordinate clauses because they do not have independent meanings and depend on principal clauses to complete their meanings. A subordinate clause consists of a clause marker.
3. Co-ordinate Clause
A clause that contains two principal clauses by joining conjunction (and, but, or) is called a coordinate clause. For example:
- I have a friend, and we stay together in the hostel.
- He is good at English, but he is not good enough at mathematics.
- Study hard, or you will fail the examination.
- She knew a person, and the person was a doctor.
- I’m playing cricket, and my brother is watching the match.
All of the sentences contain two principal clause by joining appropriate conjunctions.
Phrases
A phrase consists of words with no subject and a finite verb. A phrase does not have any independent meaning; instead, it’s part of a clause to serve as a meaningful unit. Let us see some examples:
- Being a rational person, he understands the matter.
- Walking in the street, he has reached his home.
- I love my home decoration.
- He is my brother’s friend.
- Looking out the window, I see a beautiful bird.
Note: All the underlined phrases contain without a subject and a finite verb.
Simple, Complex, and Compound Sentences

We already know that sentences are divided into three types according to their structure. They are:
- Simple sentence
- Complex sentence
- Compound Sentence
Simple Sentence
A simple sentence contains just one independent clause. A sentence containing one subject and one finite verb with an independent meaning is called a simple sentence. A simple sentence consists of one principal clause. Simple sentences are the most basic type of sentence, and they are usually short and to the point. For example:
- The cat slept.
This sentence is clear and direct. It tells us who (the cat) is and what they are doing (slept). Simple sentences don’t have to be boring, though—they’re useful for stating important facts and keeping things concise. Let’s see some other examples of simple sentences.
- The boy reads a novel.
- He sings a melodious song.
- She loves her mother.
- Mr. Abraham came here to attend the meeting.
- Jony started a business a few months ago.
Complex Sentence
A complex sentence contains one independent clause and at least one dependent (or subordinate) clause. Dependent clauses cannot stand alone as a sentence; they rely on the main clause to make sense. A sentence that contains one independent or principal clause and one or more subordinate clauses is called a complex sentence. For example:
- Although it was raining, we went for a walk.
In this sentence, “Although it was raining” is a dependent clause because it doesn’t make sense on its own. It needs the main clause, “We went for a walk,” to form a complete idea.
Complex sentences help explain relationships between ideas, such as cause and effect, contrast, or condition. Let’s see some other examples of complex sentences.
- I know a boy who is good at English.
- He is working hard so that he can make a bright future.
- Rony had a car that he bought from the market.
- Though Selina was nervous, she attended the debate.
- When I was a child, I played a lot of rural games.
Compound Sentence
A compound sentence consists of two independent or principal clauses (two complete ideas) with a coordinating conjunction—words like “and,” “but,” or “so.” This allows you to show a relationship between two equally important thoughts. For example:
- I went to the store, and I bought some groceries.
Here, we have two independent clauses: “I went to the store” and “I bought some groceries.” The coordinating conjunction “and” connects these two ideas, showing that both actions happened. Let’s see some other examples of compound sentences.
- I am a teacher, and my brother is an athlete.
- He is studying, and his friend is doing a part-time job.
- Working hard, or you will fail to make a bright future.
- Rima was a good student, but she failed the examination.
- You can read the story, or you may leave it.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the different types of sentences is essential for mastering English grammar. Examining clauses and phrases, we can categorize sentences into three main types: simple, complex, and compound.
A simple sentence contains one subject and one finite verb, conveying an independent meaning. It is the most basic and straightforward type of sentence.
On the other hand, complex sentences incorporate one principal clause and one or more subordinate clauses. These subordinate clauses rely on the principal clause to complete their intended purpose.
Compound sentences feature two principal clauses or coordinate clauses, connected by coordinating conjunctions such as “and,” “but,” or “or.” These clauses provide equal importance and contribute to the sentence’s overall meaning.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three types of sentences?
The three main types are simple, compound, and complex sentences.
What is the difference between a compound and a complex sentence?
Compound sentences connect two independent clauses, while complex sentences combine one independent and one dependent clause.
How do I know when to use a particular sentence structure?
Use simple sentences for clarity, compound sentences to connect related ideas, and complex sentences to show relationships between thoughts or actions.
Your Turn
3 Types of Sentences Quiz

Azizul Hakim is the founder & CEO of englishfinders.com. He is a passionate writer, English instructor, and content creator. He has completed his graduation and post-graduation in English language and literature.





What is the difference between dependent clause and a phrase.
A Clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a finite verb whereas a Phrase is a group of words that does not contain a subject and a finite verb.