Last updated on June 17th, 2025 at 11:05 pm
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
Quick Navigation
Have you ever stopped to think about how sentences are made in English? Every word we use has a unique role, and understanding those roles can make sentences precise and error-free. That’s where the 8 parts of speech come in. In this lesson, we’ll break down the 8 parts of speech definitions and examples so you can see how they work in real life.
Each part of speech has its own role—some words name things, some show action, and others connect ideas. When you understand these roles, English becomes much easier to learn and use.
However, if you want to improve your English grammar skills, you must know the parts of speech. Otherwise, it won’t be easy to learn English grammar more accurately. Let us know the definition of parts of speech in English grammar.
What is a Part of Speech?

When it comes to the definition of parts of speech, the simple definition is that every word in a sentence is called a part of speech. Parts of speech can be described as words that play different roles in creating a meaningful sentence. Let’s look at the sentence below.
- Wow! I see a very stunning bird flying in the sky.
This sentence clearly explains the 8 parts of speech in English. Every word in the sentence is a part of speech.
Note: A single word can function as more than one part of speech in terms of its use in sentences. For example:
- Sometimes, I dream about you.
- I have a dream to be a doctor.
In the first sentence, “dream” functions as a verb, but in the second sentence, the same word “dream” functions as a noun.
Definition of Parts of Speech by Different Scholars
- J.C. Nesfield: “The different kinds of words are called Parts of Speech.”
- Wren & Martin: “Words are divided into different kinds of classes, called Parts of speech, according to their use; that is, according to the work they do in the sentence.”
Types of Parts of Speech
There are eight types of Parts of Speech in English grammar. They are:
- Nouns
- Pronouns
- Adjectives
- Verbs
- Adverbs
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
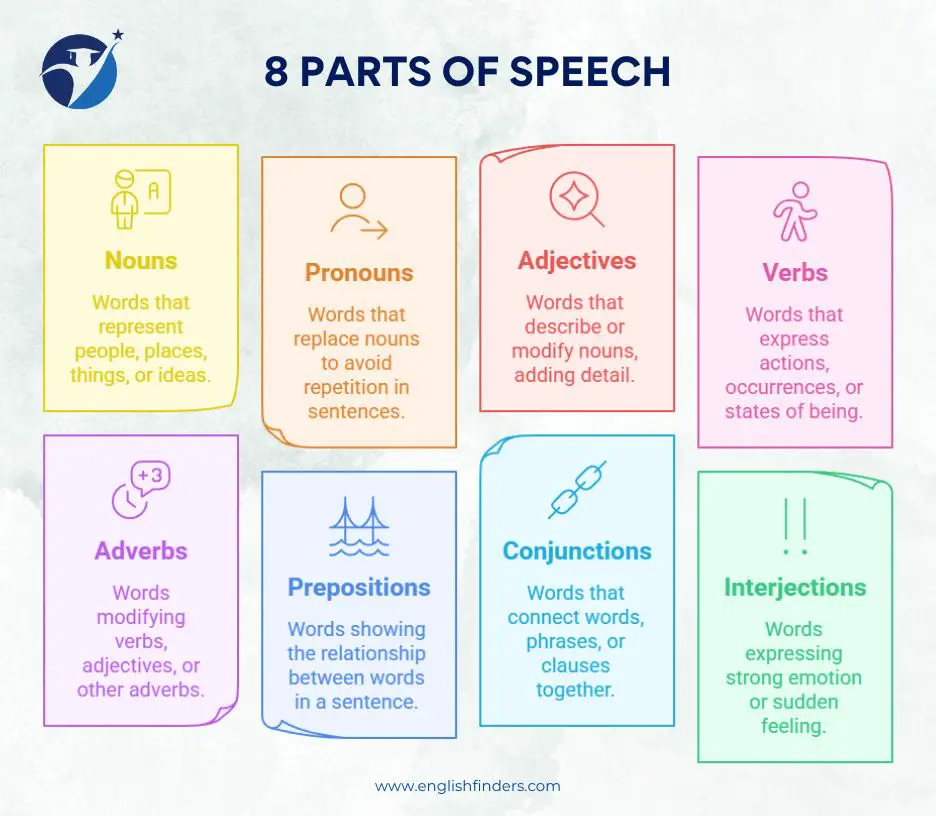
8 Parts of Speech: At a Glance
| Part of Speech | Definition | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|
| Noun | Names a person, place, thing, or idea | The teacher gave us homework. |
| Pronoun | Takes the place of a noun | She is my best friend. |
| Verb | Shows an action or a state of being | They run every morning. |
| Adjective | Describes a noun or pronoun | He wore a blue shirt. |
| Adverb | Describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb | She sings beautifully. |
| Preposition | Shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence | The deer wanders in the forest. |
| Conjunction | Joins words, phrases, or sentences together | I wanted to visit the place, but he stopped me. |
| Interjection | Shows strong emotion or feeling | Wow! This watch is amazing! |
1. Nouns
Any naming word (person, place, thing, or idea) is called a Noun. In other words, we can say that anything that names a person, place, idea, or object is a noun. Sometimes, many students think a noun is the name of a person or place only, but it can also be a thing, an idea, a feeling, an object, etc.
Let us look at some examples of nouns: John, boy, watch, country, United Kingdom, New York City, cow, army, iron, honesty, virtue, etc. Nouns are marked as bold in the below sentences for easy identification:
- John is a good boy.
- She gives an attractive watch.
- The United Kingdom is my favorite country.
- My brother lives in New York City.
- The Cow is roaming in the field.
- The army protects its homeland.
- Iron is beneficial for our daily lives.
- Honesty is a good virtue.
There are five types of nouns in English. They are:
- Proper nouns
- Common nouns
- Collective nouns
- Material nouns
- Abstract nouns
2. Pronouns
Pronouns are words that replace a noun to avoid repetition and make sentences easy to understand. If we use a single noun for every sentence, it doesn’t look good. For example, James goes to meet with his friends, and James is enjoying the party, and James recollects his old memories.
Here, we use a single noun (James) for every sentence, and that’s why it looks weird. But if we use the pronoun ‘he’ for the last two sentences instead of ‘James,’ it seems pretty good.
That’s why we need to use a pronoun instead of a noun. Let us look at examples of pronouns: he, himself, she, they, I, we, it, etc. Pronouns are marked as bold in the below sentences for easy identification:
- He is going to the market to buy a T-shirt.
- The task is done by himself.
- She plays with her classmates.
- I am the only man who understands the matter.
- We are going to arrange a free campaign.
- It was considered that he would win the trophy.
- Those are my favorite books.
There are nine types of pronouns. They are:
- Personal pronouns
- Possessive pronouns
- Reflexive pronouns
- Demonstrative pronouns
- Indefinite pronouns
- Relative pronouns
- Interrogative pronouns
- Distributive pronouns
- Reciprocal pronouns
3. Adjectives
A word used to describe a noun or pronoun is called an Adjective. In other words, an adjective usually modifies a noun or a pronoun to add extra information. Just imagine if you have a pet. How would you describe it to others? You might describe your pet as beautiful, charming, attractive, awesome, splendid, etc., right? If you use these words, you use adjectives.
Let us see some other examples of adjectives and use them in sentences. Happy, good, clever, intelligent, lazy, large, etc. Adjectives are marked as bold in the below sentences for easy identification:
- He looks like he is happy now.
- They had been playing good cricket at the time.
- Don’t try to be more clever.
- Undoubtedly, he is an intelligent person.
- This animal is so lazy.
- I saw a large building.
There are nine types of adjectives. They are:
- Proper Adjectives
- Adjectives of Quality
- Adjectives of Quantity
- Numeral Adjectives
- Demonstrative Adjectives
- Distributive Adjectives
- Interrogative Adjectives
- Possessive Adjectives
- Articles
4. Verbs
A word that expresses an action or doing something is called a Verb. Verbs are words that describe what the subject of the sentence is doing. A verb is the backbone of a meaningful sentence because, without a verb, a sentence is meaningless. For example, I ____ a smartphone. Does the sentence make any sense? Instead, if we include a verb in the blank, then the sentence becomes meaningful as “I bought a smartphone.”
Let us see some examples of verbs and use them in sentences. Am, is, are, was, were, have, has, had, can, could, should, will, go, play, read, want, sing, etc.
Verbs are marked as bold in the below sentences for easy identification:
- I am good at English.
- He is a good boy.
- They are playing on the field.
- She was suffering from a fever.
- These two boys were going to catch fish.
- I have a beautiful doll.
- They have gone to this place.
- He has done his job successfully.
- My sister had a sweet dog.
- He can do this work.
- You could attend this meeting.
- His father shall go to the field.
- You should be attentive to your studies.
- She will go to meet her friends.
- He would claim a better job.
- Read the book carefully.
- The boy wants to sing a song.
There are four types of verbs. They are:
- Auxiliary verbs
- Principal verbs
- Transitive verbs
- Intransitive verbs
5. Adverbs
A word that is used to add something to the meaning or modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb is called an Adverb. Adverbs are words that modify every part of speech except nouns or pronouns. They often describe how, when, where, or to what extent something happens.
Look at the sentence: I had a ___ handsome cat. If we fill the blank with the word “very,” then it adds an extra meaning and modifies the adjective (handsome) as well. So, the word “very” is an adverb.
Let’s see some examples of adverbs and use them in sentences. About, after, before, quickly, fast, slow, etc. Adverbs are marked as bold in the below sentences for easy identification:
- I hardly meet my friend.
- Did you see him yesterday?
- He has done his task quickly.
- They want to run fast.
- The tortoise walks slowly.
There are six types of Adverbs. They are:
- Adverbs of manner
- Adverbs of time
- Adverbs of place
- Adverbs of degree
- Adverbs of frequency
- Conjunctive adverbs
6. Prepositions
A word that is placed before a noun or a pronoun or a noun-equivalent to show its relation to any other term of the sentence is called a Preposition. Prepositions show the relationship between other words in a sentence. They often indicate time, place, and direction.
Here is an example: “I have recently visited the place and sat beside the lake.” In the sentence beside is a preposition because it shows that in which place I sat.
Let’s see some other examples of prepositions and use them in sentences. On, in, to, for, with, within, above, over, etc. Prepositions are marked as bold in the below sentences for easy identification:
- He stores his books on his bookshelf.
- They have been playing football on the field since morning.
- He goes to the market to buy some clothes.
- She is dancing with her mates.
- The plane was flying above my head.
- He couldn’t succeed in this plan over the years.
There are three types of prepositions. They are:
- Simple prepositions
- Double prepositions
- Compound prepositions
7. Conjunctions
A word that is usually used to join one word to another, one word to a clause, or one sentence to another is called a Conjunction. Conjunctions help us to build complex sentences and express our thoughts more elaborately. To get the idea more clear, let’s look at the following sentences:
- He is a poor man.
- He is very honest.
These two are simple sentences, right? If we combine the two sentences together with a conjunction then we can express the thing more clearly as, Though he is a poor man, he is honest.
Let’s see some other examples of conjunctions and use them in sentences. And, but, or, if, though, than, since, so–that, as soon as, either–or, neither–nor, etc. Conjunctions are marked as bold in the following sentences for easy identification:
- Janny and Jammy are good friends.
- He is rich but cheap-minded.
- Please read more, or you will fail the exam.
- They will be good doctors if they work hard.
- He could attend the meeting though he had enough time.
- The boy is taller than the girl.
- It has been raining since morning.
- The older man is so poor that he can’t buy enough food.
- He left the place as soon as they came.
- Either Jack or John will do the task.
- She will neither come here nor her friend.
Conjunctions are of three types. They are:
- Coordinating Conjunctions
- Subordinating Conjunctions
- Correlative Conjunctions
8. Interjections
An Interjection is a word used to express a short, sudden emotion or excitement. Interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or feelings. For example, hurrah! Alas! Oops! etc. Interjections are marked as bold in the below sentences for easy identification:
- Hurrah! We won the match.
- Alas! She is no more.
- Oops! They can’t do this job correctly.
- Wow! I got my desired laptop.
- Oh! The villagers have failed to catch the thief.
There are three kinds of Interjections. They are:
- Volitive Interjections
- Emotive Interjections
- Cognitive Interjections
Final Thoughts
These eight parts of speech— nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections are the fundamental parts of English grammar. We can make meaningful and attractive sentences by using these parts of speech.
Learning parts of speech doesn’t have to be boring or difficult. With a little practice and some real-life examples, you’ll start to notice these 8 parts of speech in everything you read and write. And the more you use them, the more natural they’ll feel.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are parts of speech?
Parts of speech are words that are assigned in a sentence to play different roles to make meaningful sentences. Every word in a sentence is a part of speech.
What are the types of parts of speech?
There are 8 parts of speech in English. They are nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
What is the difference between a noun and a pronoun?
A noun names a person, place, thing, or idea, while a pronoun replaces a noun to avoid repetition.
How can I identify verbs in a sentence?
Verbs typically describe actions, occurrences, or states of being. Look for words that show what the subject is doing or experiencing.
What part of speech is “which” in English?
The word “which” is a pronoun when it introduces a relative clause (e.g., “The book which I read was interesting”) and an adjective when it is used to specify a noun (e.g., “Which book do you want?”).
Your Turn
Parts of Speech Quiz
Have a look at these useful links:
- Stages of Child Language Development
- Definition of Language by Scholars
- Characteristics of Language
- Best English Learning Websites
- How to Learn English Quickly
- Speeches written by experts

Azizul Hakim is the founder & CEO of englishfinders.com. He is a passionate writer, English instructor, and content creator. He has completed his graduation and post-graduation in English language and literature.

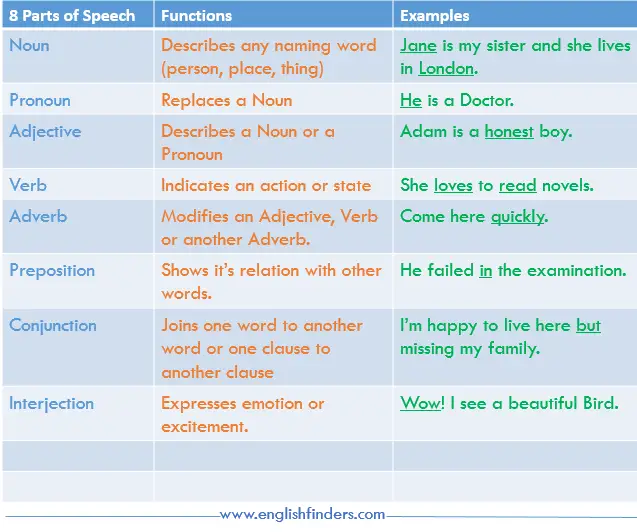




Their functions
i love this
Thanks!
GREAT!!!!!!!!!!!
Thank u!
I appreciate
Regards!
Hello
Hi
Okay, I joint
Hi
I like this grammar even my teacher also like this
Thank u!
Helped me thanks!
Welcome!
U are really a good tutor I wsh to see u
Thank you so much
You’re welcome!
Types should be discussed
We have separate lessons for each part of speech. Kindly check them out.
Define all types of noun
Very helpful! with this info, I can complete my school project. thank you so much for this!
You’re welcome!